Now Reading: How to Build an NFT Marketplace: Step-by-Step Guide
-
01
How to Build an NFT Marketplace: Step-by-Step Guide
How to Build an NFT Marketplace: Step-by-Step Guide

Planning and Discovery
The planning and discovery phase sets the foundation for a successful NFT marketplace by aligning business objectives with technical feasibility. In practice this means defining target user segments, identifying core value propositions, and documenting the journey a user takes from first visit to completed transaction. Stakeholder workshops, competitive benchmarking, and risk assessments help shape the product charter, success metrics, and the anticipated operating model. A rigorous discovery process also includes a high-level assessment of regulatory considerations, KYC/AML requirements where applicable, and potential partnerships with liquidity providers and custodians to support a trusted marketplace experience.
Beyond strategic alignment, the discovery phase should yield concrete artifacts such as a prioritized feature backlog, a data model outline, and an initial integration map for wallets, marketplaces rails, oracles, and payment rails. Establishing acceptance criteria for each feature, plus a clear definition of done for milestones, helps ensure stakeholders share a common understanding of progress. It is essential to articulate success in terms of user outcomes—for example faster NFT onboarding, lower friction during minting, and transparent provenance—rather than merely listing technical capabilities. A disciplined approach to discovery reduces risk and accelerates subsequent design and development work.
Defining Scope and Architecture
Defining scope involves choosing the minimum viable set of features that delivers meaningful value while remaining technically tractable and scalable. The MVP for an NFT marketplace typically centers on core activities: minting or listing tokens, browsing and searching catalogs, bidding or fixed-price purchases, and secure wallet interactions. As you scope features, map out user journeys for creators, collectors, and merchants, and identify the data flows, storage patterns, and latency requirements that will influence your architectural choices. This stage also explores non-functional requirements such as reliability targets, compliance constraints, and security expectations that must be baked into the design from day one.
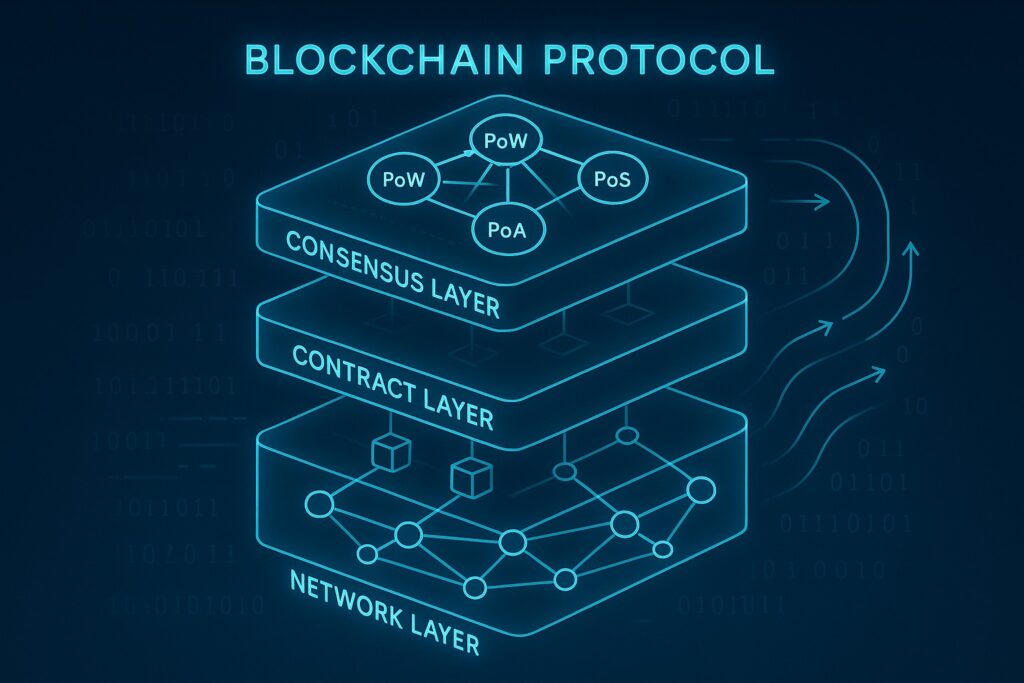
Architecturally, the system should be designed with modularity, observability, and portability in mind. A layered approach—blockchain interaction, business logic, and frontend presentation—helps isolate concerns and allows teams to evolve components independently. Consider multi-chain readiness to support cross-chain listings or bridging assets, while planning for data indexing and search capabilities, on-chain state vs. off-chain metadata, and clear ownership boundaries for governance and upgradeability. The architectural narrative should also address operational readiness, including deployment pipelines, disaster recovery concepts, and rollback procedures for critical failures.
- Modular microservices architecture to isolate wallet interactions, metadata, and marketplace logic
- Clear ownership boundaries between smart contracts, backend services, and frontend
- Event-driven data flows to enable real-time dashboards and analytics
- On-chain data with off-chain indexing for fast search and rich metadata
- Upgradeability and governance patterns that balance flexibility with security
- Security-by-design principles integrated into the architecture from the outset
Technology Stack Selection for NFT Marketplaces
Choosing the right technology stack is critical to delivering a performant, secure, and maintainable platform. The stack should support smart contract development, reliable backend APIs, scalable data storage, and a responsive user experience across devices. In many cases, blockchain-specific considerations drive core choices for the smart contract language, the blockchain network, and wallet integrations, while the rest of the stack focuses on performance, developer productivity, and ecosystem compatibility. Evaluation criteria should include developer availability, security track record, community support, tooling maturity, and the ability to meet regulatory or compliance requirements in key markets.
For the backend, consider a service-oriented approach with stateless APIs, robust authentication, and clear separation of concerns. In the frontend, a responsive framework paired with strong accessibility practices ensures a broad audience can participate. Data management strategies often combine off-chain databases for rapid queries with on-chain proofs or hashes to anchor provenance. Storage options for large artifact files (like images or 3D assets) should balance cost and durability, ideally leveraging decentralized or CDN-backed solutions with clear privacy and retention policies. A thoughtful, well-documented tech stack accelerates onboarding, reduces operational risk, and eases future expansions such as lending, staking, or enhanced marketplace features.
Smart Contracts, Standards, and Security
Smart contracts form the trust anchor of an NFT marketplace; they encode ownership, transfer rules, royalty flows, and listing mechanics. When designing these contracts, adopt established standards such as ERC-721 or ERC-1155 for token interfaces, and explore royalty extension patterns to ensure creators receive appropriate revenue streams. Security and formal verification become critical as the complexity of contract logic grows. A layered testing strategy that includes unit tests, integration tests, fuzzing, and security audits helps catch edge cases and potential exploits before deployment. It is essential to establish a robust process for contract deployment, upgradeability decisions, and a clear rollback plan in case a vulnerability is discovered after launch.
From a development perspective, inline code considerations and best practices should be followed: avoid reentrancy vulnerabilities, ensure proper access control, and implement safe approval and transfer flows. For example, you might include a minimal snippet like a standard interface token contract in your documentation or comments to illustrate pattern usage such as function transferFrom(address from, address to, uint256 tokenId) external; While the code in production will be more sophisticated, a well-documented baseline helps engineers and auditors understand intended behavior quickly.
Frontend Experience and User Experience
Delivering a compelling front-end experience for an NFT marketplace requires thoughtful UX design that translates complex on-chain interactions into intuitive flows. The onboarding journey should minimize friction for first-time users, especially those who are new to wallets or blockchain concepts. Clear guidance, progressive disclosure, and consistent visual cues help users understand terms like gas, royalty splits, and ownership transfers. The catalog and search experiences should support filters by collection, creator, price range, and edition type, while preserving fast response times and reliable pagination. Accessibility considerations and mobile-first design also ensure a broad audience can participate in the marketplace.
On the technical side, the frontend must gracefully handle asynchronous blockchain calls, provide meaningful loading states, and reconcile on-chain state with off-chain metadata. Wallet integrations should support popular wallets and offer fallbacks for users with hardware wallets to enhance security. Real-time or near-real-time updates on listing status, bids, and auctions contribute to a sense of activity and trust. Thoughtful error handling, optimistic UI patterns, and transparent status messages reduce confusion and improve confidence in complex transactions like minting new items or accepting offers.
Compliance, Security, and Operational Readiness
Compliance and security considerations evolve with the regulatory landscape and user expectations. A practical approach focuses on data privacy, user consent, and transparent disclosure of terms, fees, and ownership rights. Establish controls around Know Your Customer (KYC) where required by jurisdiction, implement robust data protection measures, and design a privacy-preserving data model for user profiles and activity history. Operational readiness includes incident response planning, change management, monitoring, and alerting. Proactive security hygiene—such as regular dependency checks, vulnerability scanning, and third-party audits—helps reduce the likelihood and impact of vulnerabilities in production.
In parallel, it is important to define governance and escalation pathways for platform changes, treasury management, and privilege operations. Governance models may range from centralized product ownership for rapid iterations to more distributed approaches that involve community input and on-chain voting. Documentation should capture deployment runbooks, environment configurations, and rollback procedures to support a resilient operation even in the face of unexpected events. Building a culture of security and compliance at every stage—from design to deployment—yields a more trustworthy platform and reduces long-term risk.
Deployment, Testing, and Launch Strategy
A disciplined deployment and testing strategy helps ensure a smooth rollout, predictable performance, and rapid incident response. Begin with a staging environment that mirrors production, including simulated traffic, wallet interactions, and contract calls, so testers can validate end-to-end flows. Create a comprehensive test plan that covers unit tests for individual components, integration tests across services, and end-to-end scenarios that reproduce typical user journeys. Emphasize performance testing to understand how the system behaves under peak load, and plan capacity for onboarding new collections, creators, and partners without compromising latency or reliability.
Spin up on-chain and off-chain test vectors, and conduct security reviews in parallel with functional testing to avoid late-stage surprises. It is advisable to perform a public or private testnet deployment before mainnet launch, incorporating a bug bounty program or third-party security audit feedback to strengthen the codebase. Prepare go-to-market activities, onboarding guides for creators and sellers, and clear documentation for developers who will build integrations with the marketplace. A well-documented launch plan reduces time-to-value for users and helps establish credibility with exchanges, custodians, and liquidity providers.
- Define release plan with milestones, success criteria, and rollback thresholds
- Prepare staging environment that mirrors production, including wallets and indexers
- Run testnet deployments for all smart contracts and backend services
- Conduct comprehensive security audits and address identified vulnerabilities
- Publish developer and user documentation, including onboarding guides
- Coordinate marketing and partner outreach to align expectations
- Monitor production performance with dashboards and alerts, ready to rollback if needed
- Provide post-launch support and iterative improvements based on user feedback
Maintenance, Governance, and Growth
Post-launch maintenance is essential to sustain trust and drive growth in a competitive market. Proactive monitoring, scheduled updates, and a clear deprecation plan for legacy features help keep the platform secure and reliable. Governance models should be designed to balance agility with safeguards, ensuring that enhancements, fee adjustments, or changes to royalty rules pass through appropriate checks and approvals. A community-driven approach—when appropriate—can improve transparency and buy-in from creators and collectors while maintaining compliance and security standards.
Growth strategies for an NFT marketplace combine technical enhancements with ecosystem development. Consider features like advanced search and discovery, collection curation, creator analytics, and enhanced provenance demonstrations that can differentiate the platform. Partnerships with marketplaces, wallets, and ecosystem participants can accelerate liquidity and reach. It is important to publish clear performance and security metrics to reassure users and investors, while maintaining a strong focus on user education and support channels to reduce friction for newcomers to blockchain-enabled commerce.
FAQ
What is the typical MVP for an NFT marketplace?
A typical MVP focuses on core capabilities: listing and purchasing NFTs, viewing provenance and metadata, wallet-based authentication, and a straightforward onboarding flow for creators. The MVP should also support a basic royalty framework, simple search and filtering, and a staging environment for testing with a limited set of collections. The goal is to validate product-market fit with measurable engagement metrics while ensuring security controls and a clean user experience.
What are common security risks and how can they be mitigated?
Common risks include smart contract vulnerabilities (reentrancy, access control flaws, and unchecked transfers), compromised wallets, and data leakage through backend services. Mitigation relies on a multi-layered approach: secure smart contract development with audits and formal verification where feasible, robust wallet and session management, least-privilege access for backend services, encrypted data storage, and comprehensive monitoring. Regular penetration testing, bug bounty programs, and rapid incident response playbooks are essential to minimize risk exposure.
How do you ensure compliance with regulations in different jurisdictions?
Compliance requires a risk-based, jurisdiction-aware approach. Establish a framework that addresses KYC/AML requirements where mandated, data privacy rules (such as regional privacy laws), and consumer protection considerations. Maintain up-to-date policies, transparent terms of service, and clear disclosures about fees and royalties. Engage legal counsel with expertise in blockchain and fintech to monitor regulatory developments and to adapt product features and data flows accordingly.
What are the major costs involved in building an NFT marketplace?
Costs include smart contract development and audits, backend infrastructure, data indexing and storage, frontend engineering, wallet integrations, and security testing. Ongoing expenses cover cloud hosting, content delivery, indexer services, and monitoring tools. Additional considerations include marketing, legal/compliance, and contingency budgets for security incidents or feature expansions. A well-structured budgeting plan aligns technical roadmaps with business milestones to prevent overspending and to support scalable growth.
How long does it take to launch a production NFT marketplace?
Timeline depends on scope, team size, and regulatory requirements, but a focused MVP typically ranges from 4 to 9 months for a production-ready platform with core capabilities. A broader feature set, multi-chain support, and mature governance models can extend timelines by several months. An iterative release strategy with early user testing, staged feature launches, and continuous integration practices helps manage risk and deliver value more rapidly.